The term human capital refers to strengthening one’s knowledge, abilities, skills and other imputes through education, training, and experiences to make them more potent and esteemed in the workforce. Today in this editorial we are going to learn what is the role of education in human capital formation.
Now I think you all are familiar with the term human capital. So, let’s move further to our next part in which we are going to discuss human capital in brief and will find out how education helps in creating and shaping human capital.
Brief Overview
Human capital refers to the collective skills, knowledge, abilities, and other intangible assets that individuals possess and contribute to economic productivity. It represents the idea that people are valuable assets, and their development and investment yield long-term benefits for both individuals and society.
Education is a fundamental driver of human capital. Formal education equips individuals with the foundational knowledge and skills necessary for various roles in the workforce. Higher education, vocational training, and continuous learning further enhance human capital, enabling individuals to adapt to changing demands in the job market. A well-educated population fosters innovation, creativity, and economic growth.
Experience and on-the-job training also play a crucial role in building human capital. Practical exposure allows individuals to apply theoretical knowledge, develop industry-specific skills, and gain insights into real-world challenges. Continuous professional development ensures that workers remain relevant and competitive in their respective fields, contributing to the overall dynamism of human capital.
Sources of Human Capital Formation
Investment in education is considered the most important source of human capital formation. Other sources of capital formation include fitness, migration, on-the-job training, and data. Let us decode it one by one.
Investment in Education
 The most effective way to enhance and extend the productive workforce in the state is by nurturing and assembling the education system. It is recognized as the core of human capital formation, and that is the cause why parents and the administration spend more on education.
The most effective way to enhance and extend the productive workforce in the state is by nurturing and assembling the education system. It is recognized as the core of human capital formation, and that is the cause why parents and the administration spend more on education.
Investment in Health
 The second primary source of human capital formation is the health sector. An unwell person will affect productivity. A few health assets are: delivering pure and secure drinking water, healing medicines, etc.
The second primary source of human capital formation is the health sector. An unwell person will affect productivity. A few health assets are: delivering pure and secure drinking water, healing medicines, etc.
Migration
 In search of high-paid jobs and better places, people migrate from one place to another. In India, unemployment is the cause of pastoral-metropolitan migration. Other professional and capable individuals like doctors, engineers, etc., relocate from one country to another in pursuit of better options.
In search of high-paid jobs and better places, people migrate from one place to another. In India, unemployment is the cause of pastoral-metropolitan migration. Other professional and capable individuals like doctors, engineers, etc., relocate from one country to another in pursuit of better options.
In both situations, migration involves transport expenses, cost of living in the relocated place, etc. The raised incomes in the new place surpass the values of migration. Therefore, acquisition in migration is another source of human capital formation.
On-The-Job Training
 To increase work productivity, many firms provide on-the-job training. This basis of income is costly, and organizations bear huge expenditures for providing on-the-job training.
To increase work productivity, many firms provide on-the-job training. This basis of income is costly, and organizations bear huge expenditures for providing on-the-job training.
Investment in Information
 Data associated with schooling and fitness can be accomplished by paying money. For example, data regarding wages are qualified for different demands.
Data associated with schooling and fitness can be accomplished by paying money. For example, data regarding wages are qualified for different demands.
Education as an Influential Factor
 Education plays a pivotal role in advancing human capital, serving as a cornerstone for individual and societal progress. Human capital encompasses the skills, knowledge, and competencies that individuals acquire through education, contributing significantly to their economic and social well-being.
Education plays a pivotal role in advancing human capital, serving as a cornerstone for individual and societal progress. Human capital encompasses the skills, knowledge, and competencies that individuals acquire through education, contributing significantly to their economic and social well-being.
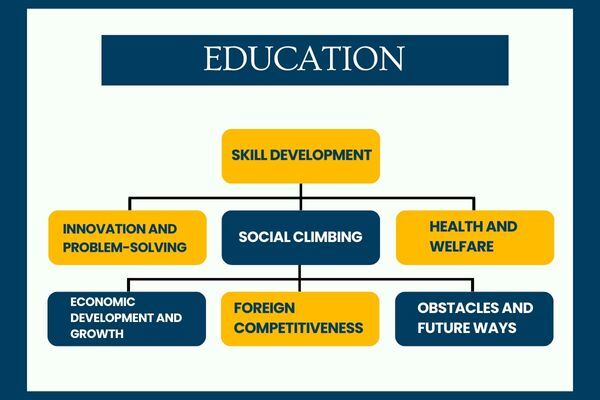
Skill Development
Firstly, education equips individuals with the necessary skills to thrive in a rapidly evolving global economy. In an era dominated by technological advancements, a well-educated workforce is crucial for innovation and competitiveness. Through formal education systems, individuals gain expertise in various fields, fostering a workforce capable of addressing complex challenges and driving economic growth.
Innovation and Problem-Solving
Moreover, education enhances critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, nurturing a population capable of adapting to change. It cultivates creativity and instills a mindset of continuous learning, vital for navigating the dynamic landscape of the modern world. A well-educated populace is more resilient and adaptable, ensuring stability in the face of economic, social, and technological shifts.
Social Climbing
Additionally, education contributes to social cohesion by promoting inclusivity and tolerance. Exposure to diverse perspectives fosters a sense of understanding and empathy, reducing societal divides. Educational institutions serve as platforms for social interaction, creating opportunities for individuals from different backgrounds to collaborate and build a cohesive, harmonious society.
Health and Welfare
Educated individuals are more likely to make informed decisions about their health, civic responsibilities, and overall well-being. This not only benefits individuals but also positively impacts communities and nations as a whole. Education is a catalyst for improved health outcomes, increased civic engagement, and the overall betterment of society.
Economic Development and Growth
Education is the key to economic growth and development. Nations with an educated population have higher rates of economic prosperity and creativity. More education means more productivity. This increases the overall economic growth and output. People with higher rates of education can easily lead the way in the advancement of technology, science, and the arts.
Foreign Competitiveness
Due to globalization, countries are intertwined with each other, given this, it is necessary to have a globally competitive workforce. Education is the key to participating effectively in the global economy. It helps in promoting capacities like language mastership, artistic sensitivity, cross-cultural cooperation, etc.
Furthermore, education provides you with a clear picture and a deeper understanding of global issues like social justice, public health, and climate change.
Obstacles and Future Ways
As we all know education is an immersive tool for the evolution of human capital. However, some obstacles are thwarting it from reaching its full prospect. The academic options available to some societies may be restrained by gender differences, poor infrastructure, and insufficient budgets.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned what is the role of education in human capital formation, and the role of education is paramount and far-reaching. Education catalyzes individual growth, societal progress, and economic development. It equips individuals with the knowledge, skills, and values necessary to navigate an ever-evolving global landscape.
Beyond the acquisition of specific subject matter, education fosters critical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and a lifelong commitment to learning. It is the cornerstone of innovation and adaptability, preparing individuals to meet the challenges of a rapidly changing world. Moreover, education contributes to the formation of a skilled and dynamic workforce, driving economic prosperity and competitiveness on a global scale.







